Ensuring robust security for healthcare facilities is a critical challenge. This essential guide dives straight into strategies for protecting patients, staff, and medical data against the evolving threats in these open-access environments. From securing entrances to safeguarding sensitive areas, you’ll learn about the technology and practices that fortify healthcare institutions, without compromising their caring mission.
Key Takeaways
- Healthcare facilities must balance accessibility with advanced security measures, utilizing local law enforcement collaboration, technology integration, and security-sensitive area protection to maintain safety for patients, staff, and assets.
- A range of technologies comprising surveillance systems, access control, and motion sensors are implemented to secure healthcare environments, with Securiteam providing innovations like one-button lockdowns, facial recognition, and integrated panic buttons.
- Specific security concerns in healthcare, such as data breaches and patient safety in sensitive areas like mental health and pediatrics, require targeted security measures, with ongoing evaluation and adoption of best practices being essential for continuous improvement.
The Significance of Security in Healthcare Facilities

Healthcare facilities are more than just buildings. They are complex environments where numerous interactions take place between different stakeholders, including:
- patients
- staff
- visitors
- care providers
A safe and secure environment is fundamental to these interactions, and security measures play an instrumental role in establishing it. Security personnel manage a range of duties from protecting against violent behavior to ensuring staff and patient safety, often acting as first responders in safety interventions.
The healthcare industry has notably prioritized security, leading to substantial investments for its enhancement. While people remain the highest priority, the security of assets and data is equally vital. A securely established environment allows healthcare facilities to concentrate on their primary mission: delivering quality healthcare services.
The Vulnerability of Healthcare Facilities
Every healthcare facility aims to be welcoming, which necessitates an open-door policy. However, this openness exposes facilities to numerous security threats, making them ‘soft targets’. The high degree of public accessibility, including numerous access points and limited security personnel, further amplifies their vulnerability.
Considering the numerous entry and exit points, implementing extensive access control systems is necessary for maintaining adequate security levels. Certain departments or regions within healthcare facilities, known as Security Sensitive Areas (SSAs), are more prone to security issues and thus need special attention.
The Role of Local Law Enforcement
Local law enforcement and emergency services are pivotal in strengthening hospital security in healthcare facilities. A robust relationship with these entities allows healthcare facilities to:
- Refine their emergency procedures and responses to incidents
- Collaborate with interdisciplinary safety teams
- Develop clear communication plans
- Form effective hospital-police partnerships
Involving law enforcement in high-risk cases, security huddles, and the development and implementation of security plans offers significant benefits for healthcare organizations. Collaboration is also essential for conducting public safety risk assessments and guaranteeing law enforcement presence when necessary for public safety.
Types of Security Measures in Healthcare Facilities

From building perimeters to interior spaces, healthcare facilities use a range of security measures to ensure safety. The security measures include:
- Security officers
- Surveillance cameras
- Appropriate lighting
- Advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, that anticipate and mitigate security threats preemptively.
These measures enhance the building perimeter and ensure the safety of the healthcare facility.
The interior security measures include modern access control systems, which contribute to healthcare security by managing entry privileges, visitor tracking, and integrating with surveillance systems to monitor sensitive areas like hospital pharmacies. The design elements of healthcare facilities also play a significant role in creating a secure yet nurturing environment for patients and staff.
Surveillance Systems
Surveillance cameras in healthcare facilities provide extensive visibility, covering areas such as:
- Waiting rooms
- Pharmacies
- Hallways
- Parking lots
This extensive coverage enables security staff to monitor larger areas and offer early warnings for potential problems.
Securiteam leverages ultra high-definition cameras and advanced video management software to enhance healthcare facility protection. This technology can rapidly detect security threats and cover vital areas. The surveillance systems extend their coverage to collectively monitor interior and exterior vulnerabilities, including sensitive regions such as parking garages and employee entrances.
Access Control Solutions
In managing access to healthcare facilities, technologies such as tap-and-go proximity cards with two-factor authentication, PINs, and biometric methods like fingerprint scans play a significant role. The integration of these access control technologies with surveillance systems maximizes protection and aids in incident investigation by providing door position and bolt position signals.
Stringent access controls and audit trails are particularly vital for staff-only areas such as nursing offices and research labs. In sensitive locations like pharmacies, where prescription medication storage demands restricted and monitored access, advanced access control systems are integral.
Motion Sensors and Alarms
Motion sensors in healthcare facilities track movement in sensitive areas and low foot traffic spaces, improving security and minimizing vulnerabilities. These facilities use various motion sensors, each employing different techniques to detect motion, such as the Coriolis effect or using air or liquid as inertial components.
To boost staff safety and effectiveness, these motion sensors should be linked with cloud-based access control systems and alarms, thereby establishing an integrated security approach. Alert systems complement these sensors by notifying staff of unauthorized movement or open access points, bolstering the overall security in healthcare settings.
Securiteam Security Solutions for Healthcare Facilities
Securiteam, with over 15 years of experience, provides advanced security solutions to healthcare facilities. Their offerings include:
- Connected business technologies
- Virtual security guards
- Full-service access controls
- Automated gate controls
- Comprehensive response and management systems
To manage access to Sensitive Security Areas (SSAs), Securiteam provides security systems equipped with analytics and insights, offering valuable data on who is accessing these critical zones.
Securiteam also brings innovation to pediatric patient security through cloud-based access controls, single-dashboard management, and over-the-air updates. These advancements ensure security and compliance with HIPAA standards.
One Button Facility Lockdown
In an emergency, every second counts. Securiteam’s one-button lockdown system is designed to quickly secure rooms or areas in a healthcare facility during such times. The solutions can be customized to address specific operational and security requirements of different hospital areas.
Role-based access control and lockdown options play a vital role in fortifying security in sensitive hospital spaces during emergencies. The access control systems should be cloud-based, facilitating remote management and seamless integration with other security measures.
Facial Recognition Software
AI-powered facial recognition software in healthcare offers several benefits, including:
- Secure access to sensitive areas, allowing only those with proper credentials to enter
- Streamlining administrative processes by tracking patient and visitor entry and exit records
- Maintaining accurate attendance records of employees through integration with time clock systems
Securiteam Security Solutions implement an AI system that tracks individual movements and behavior, allowing for the creation of custom security protocols based on the tracked individual. Smart medicine cabinets equipped with this technology restrict access to authorized personnel at scheduled times for enhanced medication safety.
Integrated Panic Button
During emergencies, Securiteam’s integrated panic button feature can be a lifesaver. The panic button is integrated with video instruction to guide immediate response during emergencies.
The blend of panic buttons and video feeds enables swift alerting of onsite security teams and police, promoting quick incident responses. This feature is another testament to how advanced technology can significantly enhance security in healthcare settings.
Addressing Specific Security Concerns in Healthcare Environments
While the general security measures discussed so far are critical, healthcare facilities also face specific security concerns. These include:
- Alarm fatigue
- Data breaches
- Threats of violence
- Unwanted visitors
- Drug thefts
All of these issues necessitate specific measures to protect patient possessions and prescription drugs.
Implementing access control systems based on the principle of least privilege helps protect hospital assets by managing visitor access and maintaining event logs. Furthermore, enhancing patient, staff, and visitor safety can be achieved through privacy protection measures and by preventing incidents like infant abductions.
Protecting Personal Health Information
In the era of digital health records, protecting personal health information has become a significant concern. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandates the privacy and security of patient medical data, especially for data transmitted over the internet. Violations of HIPAA are subject to enforcement through audits and must be self-reported to the Office for Civil Rights under the Department of Health and Human Services.
To prevent such violations and secure sensitive patient information, healthcare facilities need to enhance their cyber and physical security measures, specifically to prevent data breaches.
Ensuring Safety in Mental Health Areas
Mental health units within healthcare facilities present unique security challenges due to the high risk of patient unpredictability and violence. Risk mitigation involves creating a safe physical environment with features such as tamper-proof fixtures, unbreakable windows, and reduction of ligature points.
Real-time monitoring technologies assist in the fast localization of wander-prone patients, aiding in the prevention of incidents like patient elopement. Additionally, emotion recognition capabilities of facial recognition software play a growing role in monitoring mental health patients’ wellbeing, providing valuable data for psychotherapeutic applications.
Infant Security and Pediatric Protection
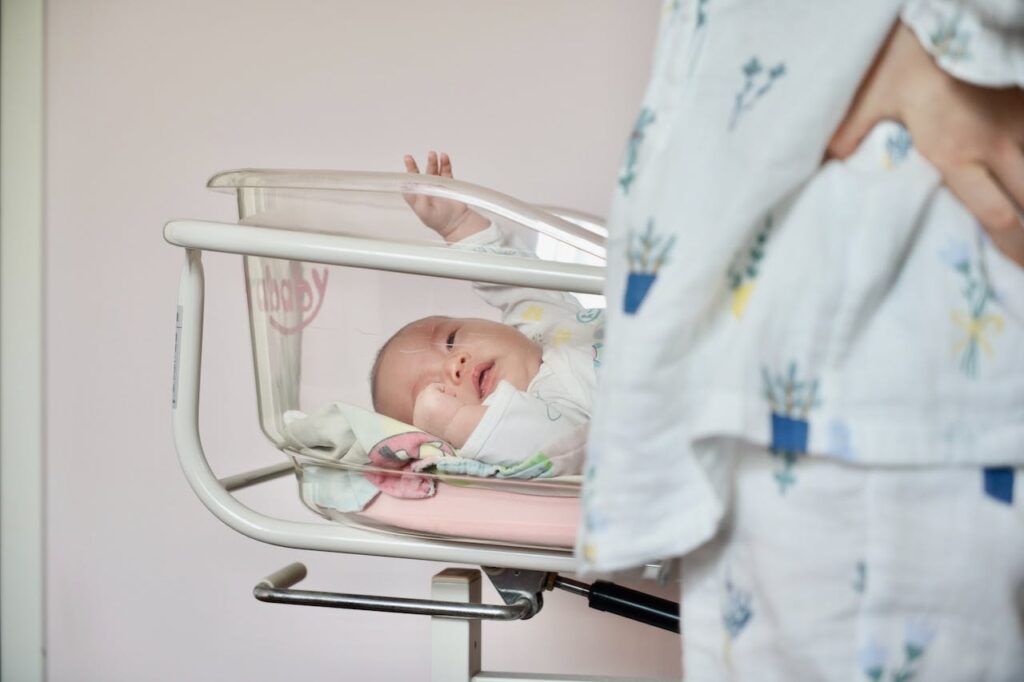

Ensuring the safety of newborns and pediatric patients is a critical aspect of healthcare security. The Hugs solution is a leading infant security system, protecting 2 million infants annually in over 1780 hospitals around the world. This system provides hospital-wide security, featuring continuous monitoring of infants and throughout the facility.
The Hugs solution includes:
- The Hugs component, which provides continuous monitoring of infants to ensure their safety and well-being
- The Kisses component, an automatic mother-infant matching feature that works in harmony with traditional ID bands to ensure correct matches
- Infant tags that are designed to be both user-friendly for staff and safe for babies, facilitating rapid attachment and system activation.
Best Practices for Implementing Security Systems in Healthcare Facilities
The Security Industry Association (SIA) provides a comprehensive guide to best practices for implementing security systems in healthcare environments. These best practices include minimizing unnecessary access points, implementing role-based access control, and using the Good-Better-Best (G-B-B) model to evaluate security systems.
These best practices advocate for a variety of security measures such as:
- Physical security systems: access control systems
- Communication systems
- Fire and life safety systems
- Video surveillance
- Perimeter/intrusion detection
- Network infrastructure
- Security information and event management systems
Compatibility and Centralized Management
One of the critical elements of effective security systems is ensuring compatibility of software and hardware. The G-B-B model emphasizes upgrading security systems and ensuring basic systems integration to maintain compatibility. Old hardware that cannot support the latest operating systems can lead to performance issues with new applications, hampering the security infrastructure.
Centralized management of security solutions, as provided by Securiteam Security Solutions, enables complete control over the facility, bolstering overall security. Some benefits of centralized management include:
- Complete control over the facility’s security
- Modern access control systems that allow for role-based privileges and include lockdown features
- Optimization of security management for 24/7 hospital operations
Concentric Circles of Protection
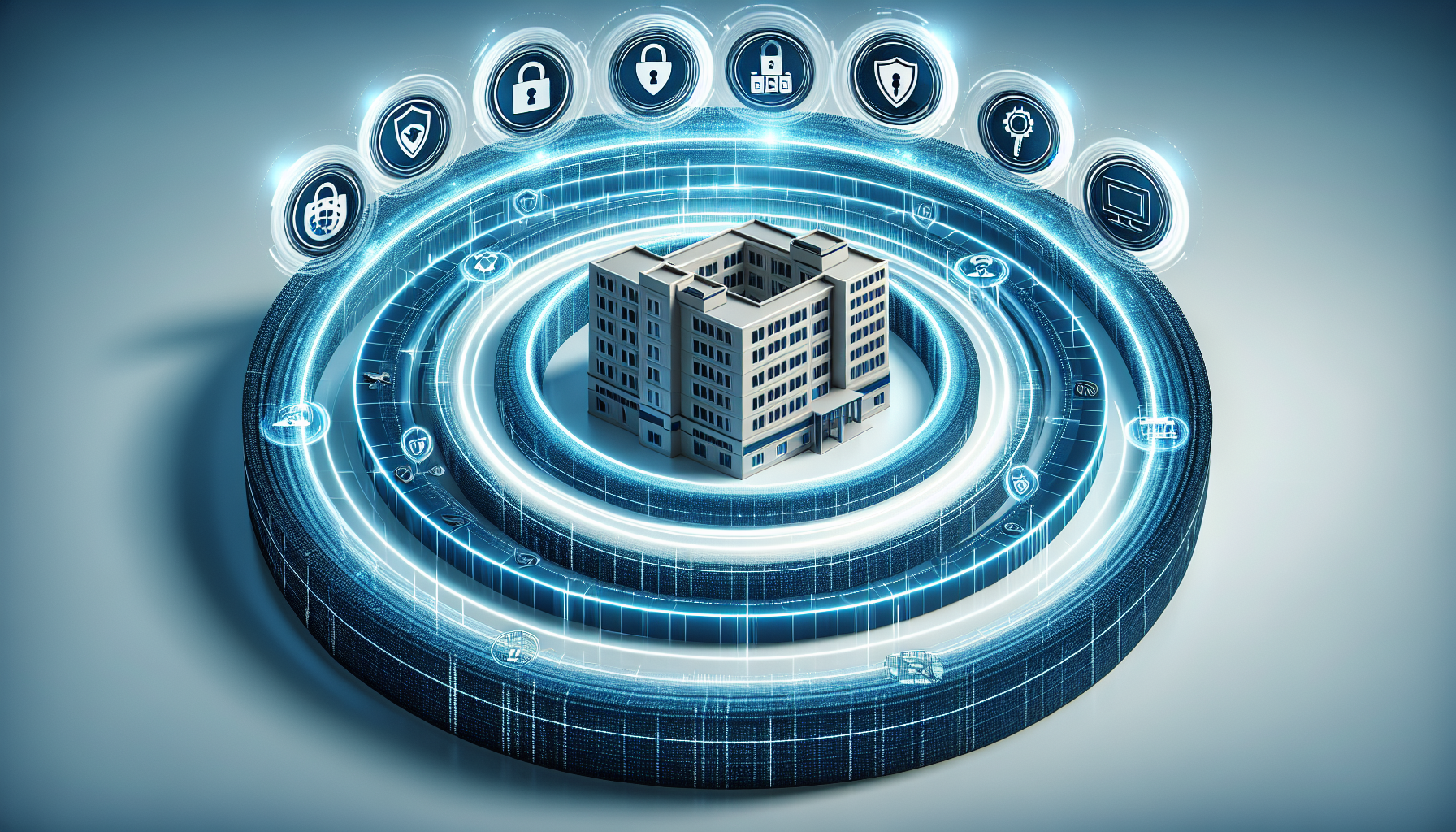

The ‘Concentric Circles of Protection’ strategy, also known as ‘Security in Depth’, is a best practice for organizing physical security in healthcare settings. Each layer of this security model serves to deter, detect, and delay intruders, providing a chance for security response before they can reach sensitive or high-value areas.
Multiple layers of security ensure no single point of failure; if one layer is compromised, others continue to protect, making it more challenging for an intruder to progress further. It is advised for healthcare facilities to implement a minimum of three layers, but ideally five or more, between the exterior and any valuable or critical asset to enhance security.
Ongoing Evaluation and Improvement
Continuous evaluation and improvement of security systems are essential for maintaining a secure healthcare environment. The guide emphasizes the necessity of continuously evaluating security systems to ensure they deliver a measurable return on investment while adapting to new technologies.
Training healthcare facility personnel is instrumental in deploying security measures. The cultivation of security awareness among employees acts as an unseen but vital layer of defense, boosting the facility’s overall security.
A structured 3-step risk mitigation process that includes accountability measures, access control, and practical scenario exercises is instrumental in addressing security risks that may otherwise be overlooked.
Summary
In conclusion, the importance of security in healthcare facilities cannot be overstated. From general measures such as surveillance systems and access control to specific solutions for mental health areas and infant security, all these aspects play a crucial role in maintaining a safe and secure environment. Implementing best practices, ensuring compatibility and centralized management, adopting the ‘Concentric Circles of Protection’ strategy, and maintaining ongoing evaluation and improvement are essential steps towards enhancing security in healthcare facilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is health care security?
Healthcare security refers to the protection of data, computers, and networks used by healthcare providers and companies, driven by regulations such as HIPAA.
What are the security controls in hospitals?
Hospitals use sturdy doors, reinforced windows, secure cabinets, and electronic locks to safeguard equipment, medication, and sensitive documents, limiting access to authorized personnel only.
What is the role of security in healthcare facilities?
Security in healthcare facilities is crucial for creating a safe environment for patients, staff, and visitors. It involves measures such as surveillance systems, access control, and motion sensors.
Why are healthcare facilities considered ‘soft targets’?
Healthcare facilities are considered ‘soft targets’ because they have an open-door policy and multiple access points, making them vulnerable to security threats.
What are some specific security concerns in healthcare environments?
In conclusion, specific security concerns in healthcare environments include alarm fatigue, data breaches, threats of violence, unwanted visitors, and drug thefts, which necessitate comprehensive security measures.